
GST Rate Changes & Their Impact on Indian Markets
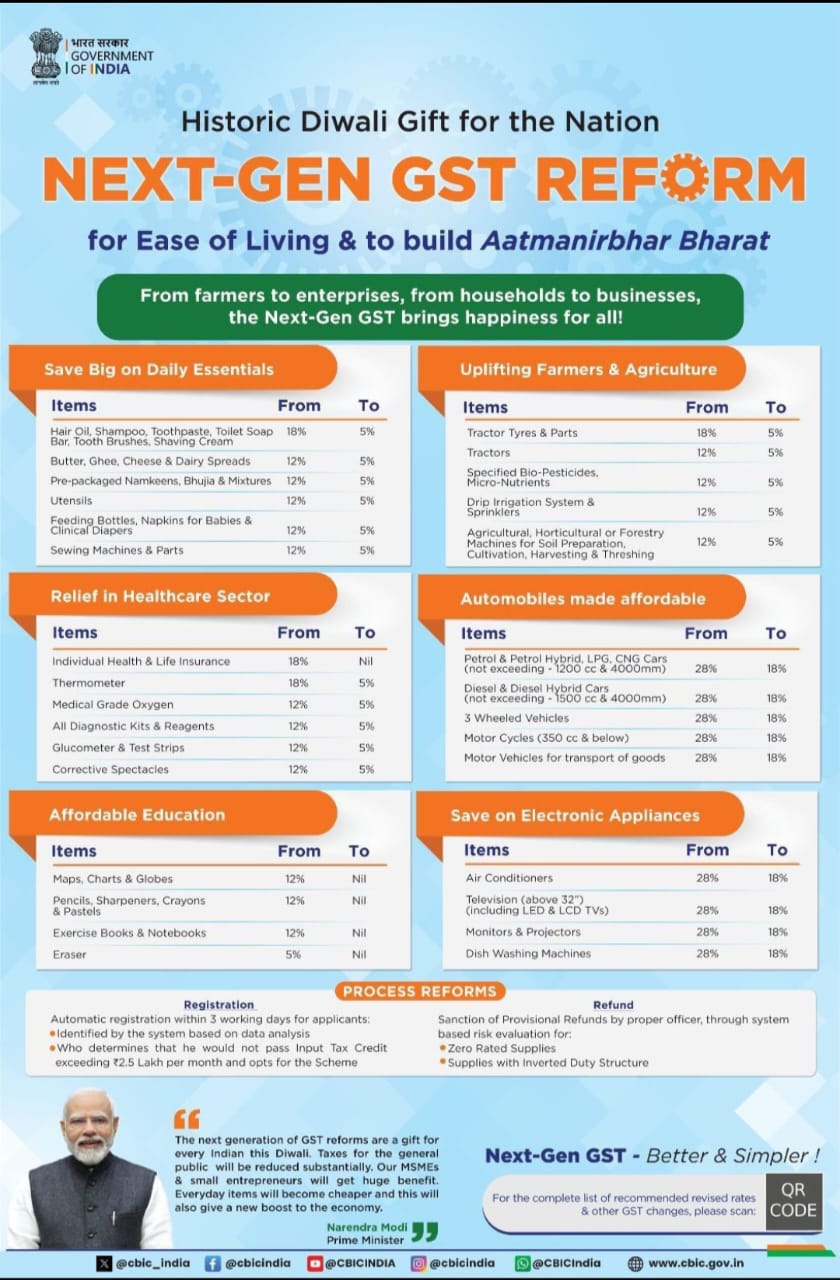
The Government of India’s ambitious Next-Gen GST reform package, announced as a “Historic Diwali Gift for the Nation,” represents one of the most comprehensive tax restructuring initiatives since GST implementation. This sweeping reform touches virtually every sector of the economy, creating ripple effects that savvy investors can leverage through strategic mutual fund investments. GST rate changes will be implemented from September 22, 2025
Understanding the Reform Landscape
The Next-Gen GST reforms focus on rate rationalization across multiple sectors, with the primary objective of reducing the tax burden on essential goods and services while streamlining compliance procedures. The reforms affect over six major sectors, creating both direct cost benefits for consumers and indirect investment opportunities for mutual fund investors.
Sector-Wise Impact Analysis
FMCG and Daily Essentials: The Consumer Revolution
The FMCG sector emerges as the biggest beneficiary of these reforms. GST rates on daily essentials have been slashed from 12-18% to just 5%, covering items like hair oil, shampoo, toothpaste, soap bars, butter, ghee, and dairy spreads. This dramatic reduction translates to immediate cost savings for manufacturers and enhanced affordability for consumers.
Market Impact: The price reduction on everyday items is expected to trigger increased consumer demand, directly boosting FMCG company revenues. Companies like Hindustan Unilever, ITC, Nestle, and Dabur are positioned to benefit significantly from higher volume sales. The affordability factor will likely expand market penetration, particularly in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
Investment Implications: FMCG-focused mutual funds and diversified equity funds with substantial FMCG holdings stand to gain considerably. The sector’s defensive nature, combined with growth acceleration, makes it attractive for both aggressive and conservative investors.
Agriculture and Rural Economy: Powering India’s Backbone
Agricultural inputs and machinery have received substantial tax relief, with GST rates reduced from 12-18% to 5-12% on critical items including tractor parts, bio-pesticides, drip irrigation systems, and agricultural machines.
Market Impact: Lower input costs directly improve farm economics, potentially increasing farmer income and rural purchasing power. This creates a positive cycle where increased agricultural productivity leads to higher rural consumption, benefiting the entire rural economy ecosystem.
Investment Implications: Mutual funds with rural and agribusiness exposure, including those investing in tractor manufacturers, fertilizer companies, and rural-focused banks, present compelling opportunities. Funds focusing on consumption themes and rural development are particularly well-positioned.
Healthcare: Democratizing Wellness
The healthcare sector receives significant relief with individual health and life insurance premiums becoming GST-exempt (previously 18%). Essential medical equipment like thermometers, oxygen concentrators, diagnostic kits, and corrective spectacles now carry just 5% GST instead of 12-18%.
Market Impact: Reduced healthcare costs are expected to increase insurance penetration, while lower medical equipment prices make healthcare more accessible. This structural shift supports the broader healthcare ecosystem, from insurers to medical device manufacturers.
Investment Implications: Healthcare-focused mutual funds, pharma funds, and schemes investing in insurance companies present attractive long-term opportunities. The demographic dividend and increased health consciousness further strengthen the investment thesis.
Automotive Sector: Accelerating Growth
The automotive industry receives a substantial boost with GST rates reduced from 28% to 18% on hybrid cars, three-wheelers, motorcycles, and commercial vehicles.
Market Impact: A 10 percentage point reduction in GST significantly impacts vehicle affordability, particularly for commercial vehicles and two-wheelers. This is expected to boost auto sales across segments, supporting both OEMs and auto component manufacturers.
Investment Implications: Auto-focused mutual funds and manufacturing-themed schemes become more attractive. The policy support for hybrid vehicles also creates opportunities in the electric and hybrid vehicle ecosystem.
Electronics and Consumer Durables: Digital India Push
Consumer electronics receive major relief with GST on air conditioners, large televisions, monitors, projectors, and dishwashing machines reduced from 28% to 18%.
Market Impact: The 10% reduction in GST makes consumer electronics more affordable, likely spurring demand in the durables segment. This supports the Digital India initiative and benefits both domestic and international electronics companies.
Investment Implications: Technology funds, consumption-themed mutual funds, and schemes focused on the consumer discretionary sector stand to benefit from increased demand and improved margins.
Education: Building Human Capital
The education sector receives complete GST exemption (nil rate) on essential items including maps, charts, globes, pencils, sharpeners, crayons, pastels, exercise books, notebooks, and erasers, which previously carried GST rates of 5-12%.
Market Impact: The complete elimination of GST on educational essentials reduces the cost burden on families and educational institutions. This supports the government’s emphasis on education accessibility and skill development, particularly benefiting students from lower-income households.
Investment Implications: While the direct investment impact may be limited due to the smaller market size, funds with exposure to educational content providers, stationery manufacturers, and ed-tech companies may see improved operating environments and potential volume growth.
Strategic Mutual Fund Investment Opportunities
Sector-Specific Fund Recommendations
FMCG Funds: With the sector receiving maximum benefit, FMCG-focused funds offer immediate opportunity. Look for funds with exposure to market leaders who can capitalize on increased demand.
Consumption Funds: These funds typically hold a diversified portfolio across beneficiary sectors including FMCG, automobiles, and consumer durables, providing comprehensive exposure to reform benefits.
Rural and Agriculture Funds: Funds focusing on rural themes and agribusiness can capitalize on improved farm economics and increased rural purchasing power.
Healthcare Funds: Long-term structural benefits in healthcare make specialized healthcare funds attractive for patient investors.
Diversified Investment Strategies
Large-Cap Funds: Established companies in beneficiary sectors are likely to see immediate impact, making large-cap funds with appropriate sector allocation attractive.
Multi-Cap Funds: These provide exposure across market capitalizations, capturing benefits from both large established players and emerging mid-cap companies in reformed sectors.
SIP Strategy: The phased implementation of reforms makes SIP investments particularly attractive, allowing investors to benefit from gradual market adjustment and potential volatility.
Process Reforms: The Hidden Catalyst
The reforms extend beyond rate changes to include crucial process improvements. Automated registration within three working days, enhanced refund mechanisms, and simplified compliance reduce business operational costs across sectors.
These process reforms create a more business-friendly environment, potentially improving the overall ease of doing business and supporting economic growth across all sectors.
Investment Timing and Strategy
With the reforms taking effect from September 22, 2025, investors have a clear timeline to position their portfolios strategically. The staggered market impact of GST reforms creates multiple entry points for investors. Immediate beneficiaries like FMCG and consumer durables may see quick gains post-implementation, while sectors like healthcare and agriculture may show sustained long-term growth as the reforms gain traction.
Short-term Strategy: Focus on FMCG and consumer discretionary funds for immediate impact following the September implementation.
Long-term Strategy: Build positions in healthcare, rural, and infrastructure funds for sustained growth as the policy effects compound over time.
Balanced Approach: Diversified equity funds and multi-cap funds provide exposure to all beneficiary sectors while maintaining risk balance during the transition period.
Conclusion
The Next-Gen GST reforms represent a paradigm shift in India’s tax structure, creating substantial investment opportunities across multiple sectors. For mutual fund investors, this presents a rare opportunity to align investment strategies with significant policy support.
The key to maximizing these opportunities lies in understanding sector-specific impacts and choosing appropriate mutual fund categories. Whether through sector-specific funds or diversified schemes, investors can participate in India’s structural transformation while building long-term wealth.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only. Investors should consult with qualified financial advisors and conduct thorough research before making investment decisions. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Follow us on Instagram @funds.cart
www.fundscart.com